Localization is used to translate the application to several languages. Almost all of the apps needs localization for better user enagement.
Here we are going to implement Localization in a sample-simple flutter application.
Initial Setup for Localization
Add following dependancy in pubspec.yaml
provider: ^4.0.5Provider is used to update and manage the state of the application, I am using provider and view model class to switch languages.
Add following files
app_localization.dart
AppLocalization class contains following functions
loadfunction will load the string resources from the desired Locale as you can see in the parameter.offunction will be a helper like any other InheritedWidget to facilitate access to any string from any part of the app code.translatethis method is used to translate words from the json files
add the file in lib/localization folder
import 'dart:convert';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
import 'package:localization_app/localization/supportedLanguages.dart';
class AppLocalization {
// Helper method to keep the code in the widgets concise
// Localizations are accessed using an InheritedWidget "of" syntax
static AppLocalization of(BuildContext context) {
return Localizations.of<AppLocalization>(context, AppLocalization);
}
// Static member to have a simple access to the delegate from the MaterialApp
static const LocalizationsDelegate<AppLocalization> delegate =
_AppLocalizationsDelegate();
Map<String, String> _localizedStrings;
Future<dynamic> load(locale) async {
// Load the language JSON file from the "lang" folder
// print("DATAAA" + 'assets/language/${locale.languageCode}.json');
String jsonString = await rootBundle
.loadString('assets/language/${locale.languageCode}.json');
Map<String, dynamic> jsonMap = json.decode(jsonString);
_localizedStrings = jsonMap.map((key, value) {
return MapEntry(key, value.toString());
});
return true;
}
// This method will be called from every widget which needs a localized text
String translate(String key) {
return _localizedStrings[key] ?? "Missing Localized String";
}
}
class _AppLocalizationsDelegate extends LocalizationsDelegate<AppLocalization> {
// This delegate instance will never change (it doesn't even have fields!)
// It can provide a constant constructor.
const _AppLocalizationsDelegate();
@override
bool isSupported(Locale locale) {
// Include all of your supported language codes here
return supportedLanguages.contains(locale.languageCode) ||
supportedLanguages.contains(locale);
}
@override
Future<AppLocalization> load(Locale locale) async {
// AppLocalizations class is where the JSON loading actually runs
AppLocalization localizations = new AppLocalization();
await localizations.load(locale);
return localizations;
}
@override
bool shouldReload(_AppLocalizationsDelegate old) => true;
}
supported_languages.dart
add the file in lib/localization folder
import 'dart:ui';
const supportedLanguages = [
const Locale.fromSubtags(languageCode: 'en'), // generic Chinese 'zh'
const Locale.fromSubtags(
languageCode: 'zh',
scriptCode: 'Hant'), // generic traditional Chinese 'zh_Hant'
];
Translated Json files
- en.json file includes all the words for English
- zh.json file has all the words in Chinese
add this file in assets/language folder
en.json
{
"TITLE":"Localization Example"
}zh.json
{
"TITLE": "本地化示例"
}Now we have added all required files for Localization.
Lets move to the implementation part
Implement Localization in App
add the following code in main.dart
import 'package:flutter/cupertino.dart';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:localization_app/localization/LocalizationKeys.dart';
import 'package:localization_app/localization/app_localizations.dart';
import 'package:localization_app/localization/supported_languages.dart';
import 'package:localization_app/view_models/settings_view_model.dart';
import 'package:provider/provider.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MultiProvider(
providers: [
ChangeNotifierProvider(
create: (context) => SettingsViewModel(),
),
],
child: Consumer<SettingsViewModel>(
builder: (context, viewModel, child) {
return MaterialApp(
supportedLocales: supportedLanguages,
localizationsDelegates: [
AppLocalization.delegate,
DefaultMaterialLocalizations.delegate,
DefaultWidgetsLocalizations.delegate,
DefaultCupertinoLocalizations.delegate,
],
locale: viewModel.getLocale,
title: 'Localization Example',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(title: 'Localization Example'),
);
},
),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
@override
_MyHomePageState createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Consumer<SettingsViewModel>(builder: (context, model, child) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Text(
AppLocalization.of(context).translate("TITLE"),
),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
model.setLocale(model.getLocale == Locale("en")
? Locale("zh")
: Locale("en"));
},
child: Text("Change Language"))
],
),
),
),
);
});
}
}
- HomePage has a Text widget and a ElevatedButton to switch languages.
- In onPress of ElevatedButton we are switching languages based on the current language.
Don’t forget Add following line in pubspec.yaml
assets:
- assets/language/Now we are all set to run the Application
Output
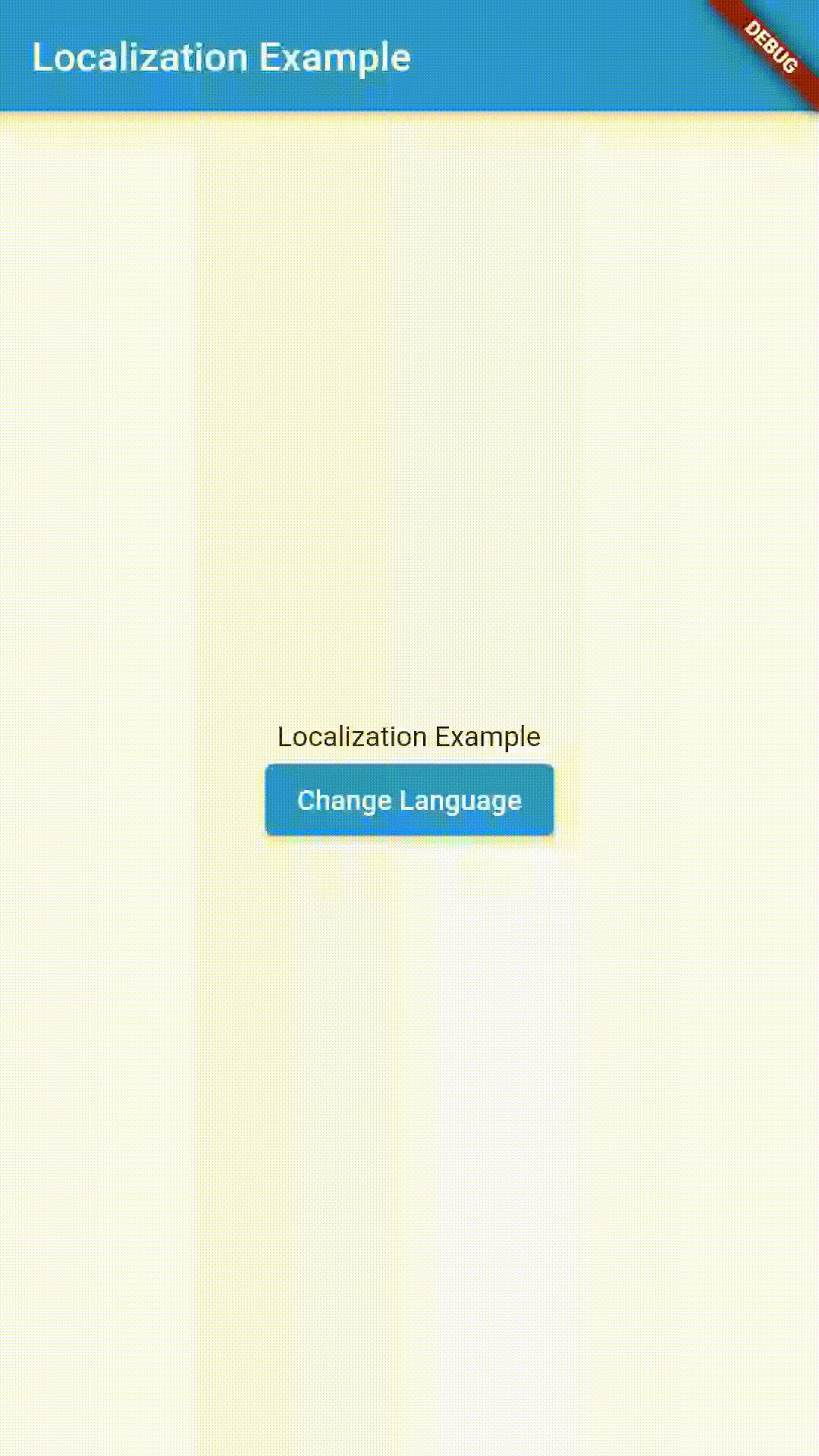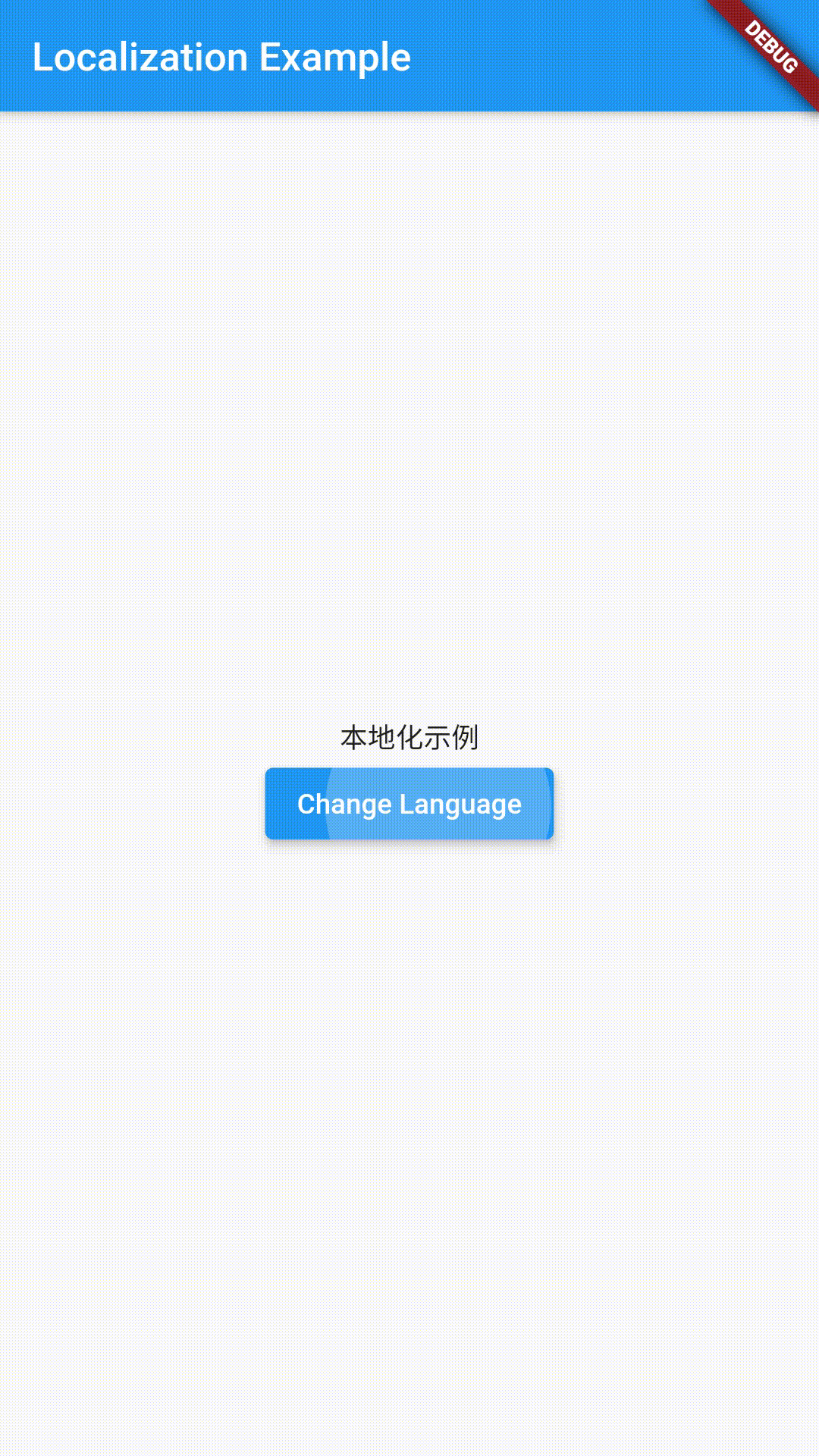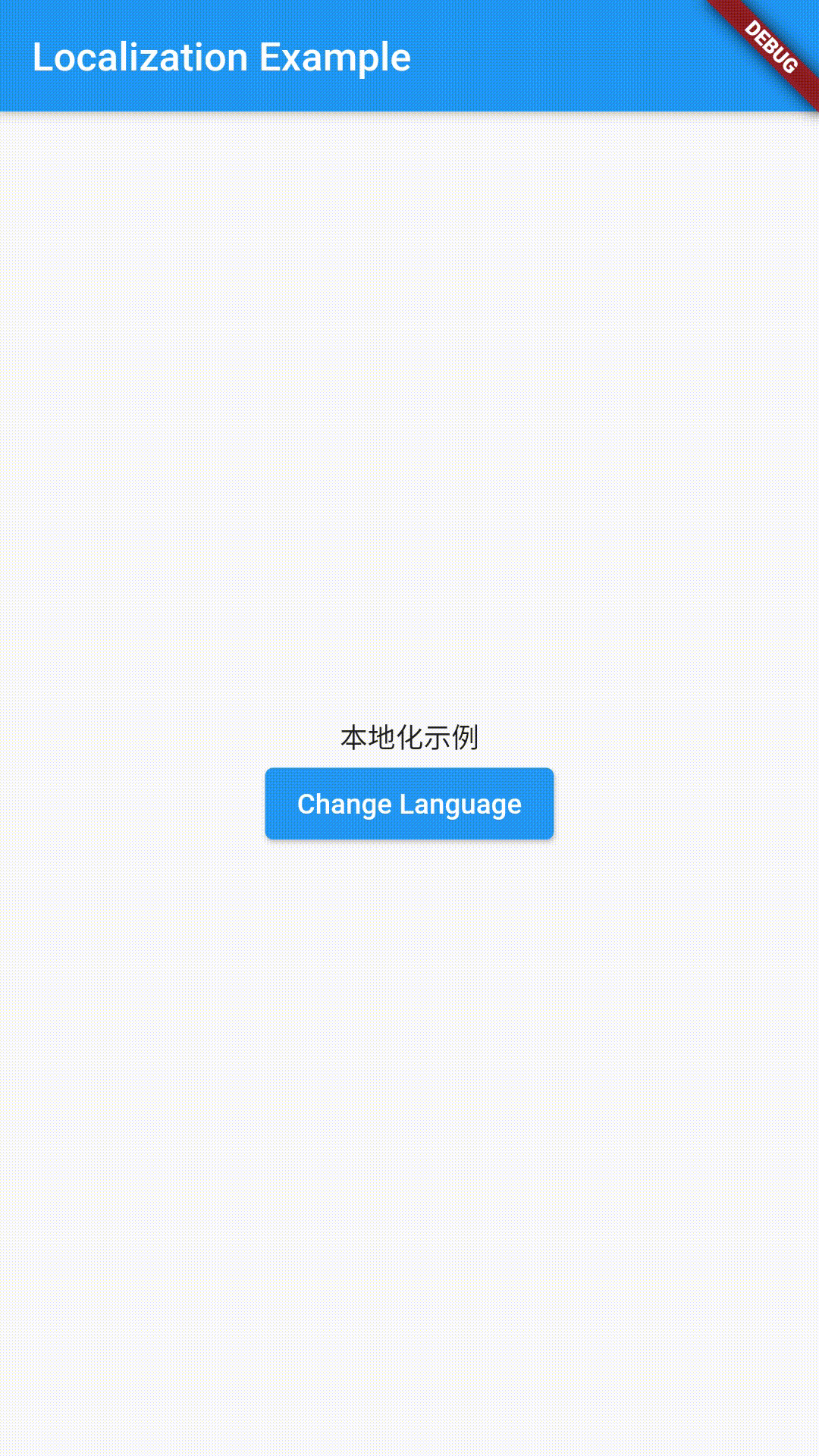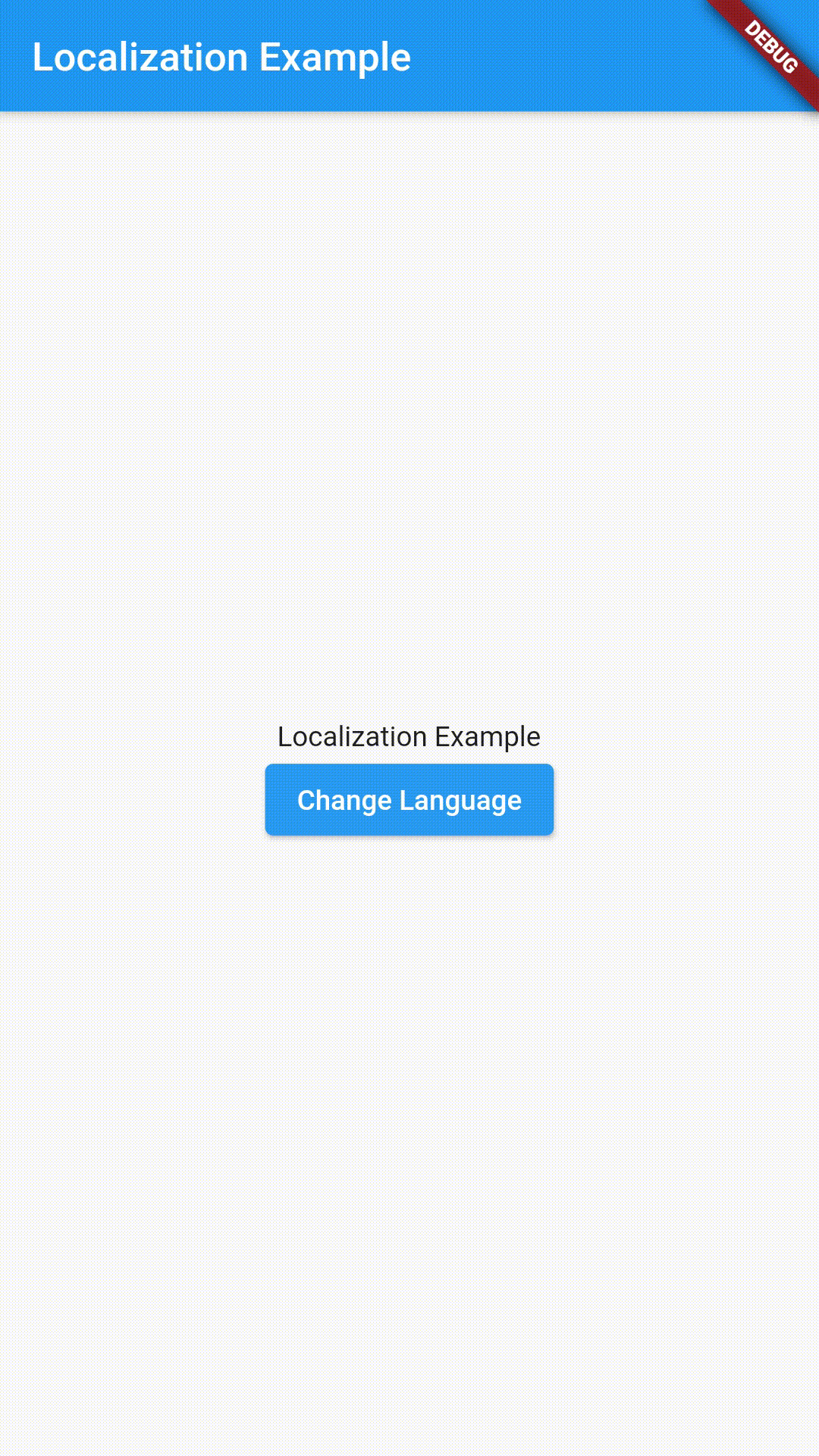
The full source code is available here.

That’s it!! Thanks for Reading
